Instead a messenger RNA mRNA molecule is synthesized from the DNA and. Which best describes the storage of the genetic code.

Genetic Code Chart Coding Genetics Biology Lessons
Genetic code refers to the instructions contained in a gene that tell a cell how to make a specific protein.
. It is used to build an organisms structures. CAM plants have adapted to very dry climates by opening their stomata only during the day. Code is a Triplet.
Ambiguous but not redundant. A gene is a segment of DNA a condensed DNA molecule makes up a chromosome a chromosome is inside a nucleus and a nucleus is contained within a cell. The Central Dogma describes the flow of genetic information in the cell from genes to mRNA to proteins.
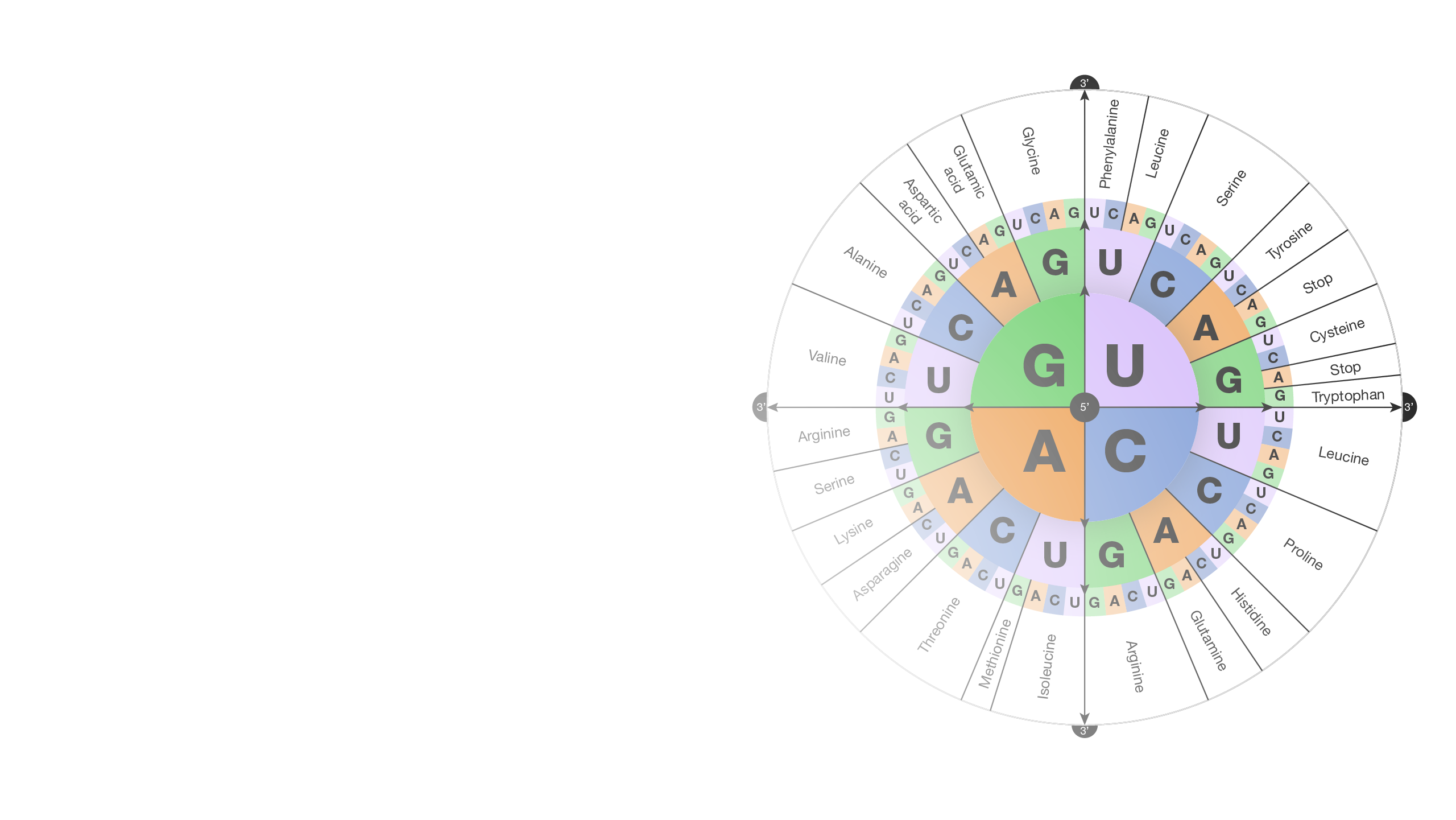
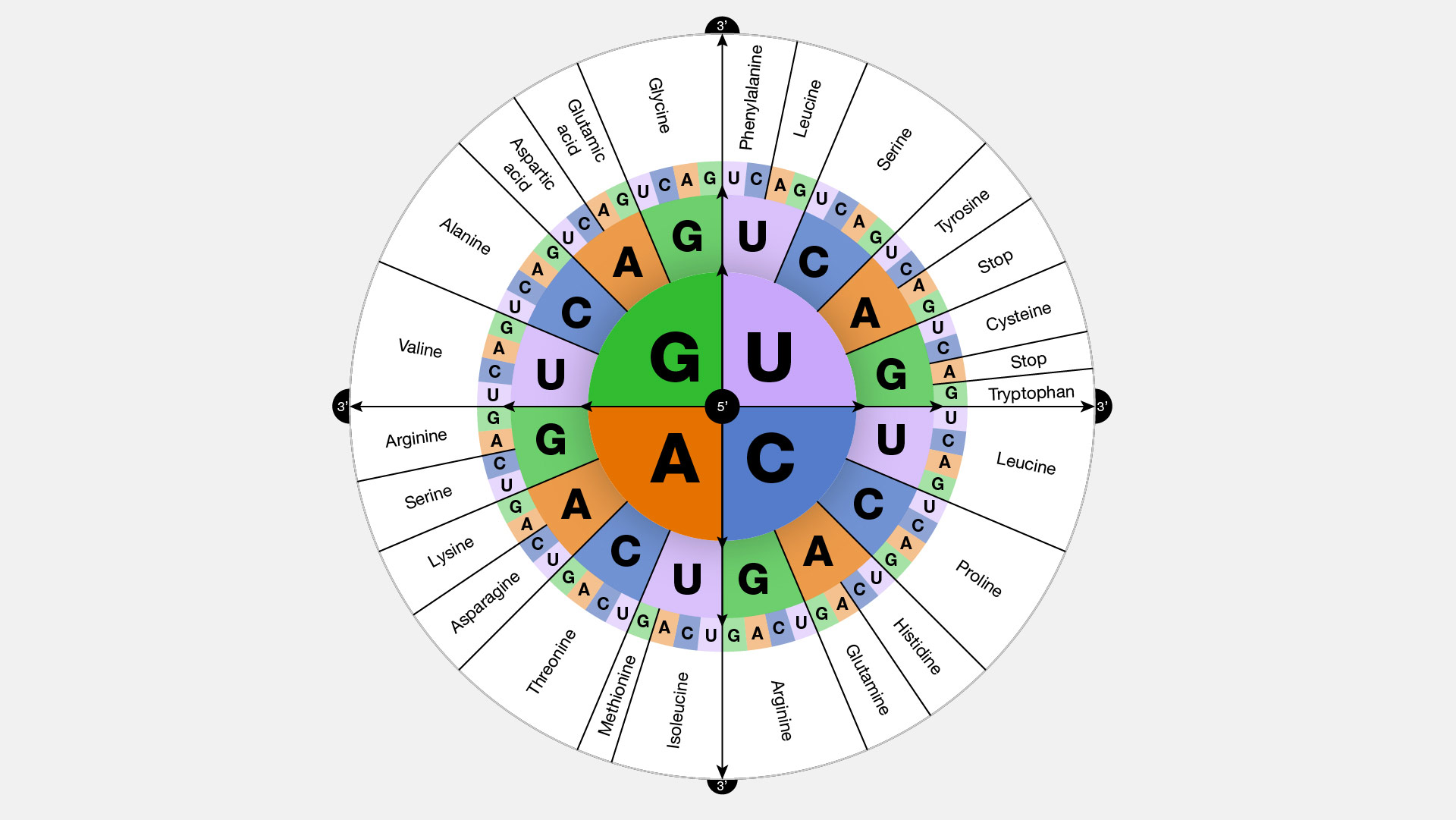
As pointed out earlier the coding units or codons for amino acids comprise three letter words 4 x 4 x 4 or 4 3 64. It is typically discussed using the codons found in mRNA as mRNA is the messenger that carries information from the DNA to the site of protein synthesis. The relationship between a nucleotide codon and its corresponding amino acid is called the genetic code.
They link the amino acids in an mRNA-specified messenger RNA order using tRNA transfer RNA. The Central Dogma describes the flow of genetic information in the cell from genes to mRNA to proteins. The genetic code is best described as O both ambiguous and redundant.
Both ambiguous and redundant. The genetic code is nearly universal and the arrangement of the codons in the standard codon table is highly non-random. Three stop codons mark the end of a protein.
The genetic code refers to the DNA alphabet A T C G the RNA alphabet A U C G and the polypeptide alphabet 20 amino acids. The genetic code is best described as a. Which characteristics describe the genetic code of humans.
It is a protein. We analyze your DNA fo. Three bases form an amino acid also known as a codon.
What is a Genetic Code. Each genes code uses the four nucleotide bases of DNA. Genetic code the sequence of nucleotides in deoxyribonucleic acid DNA and ribonucleic acid RNA that determines the amino acid sequence of proteins.
Neither ambiguous nor redundant. The genetic code refers to the DNA alphabet A T C G the RNA alphabet A U C G and the polypeptide alphabet 20 amino acids. Genetic Code Definition.
Which statements describe the genetic code. O ambiguous but not redundant. Given the different numbers of letters in the mRNA 4 A U C G and protein alphabets 20 different amino acids one nucleotide could not correspond to one amino acid.
View the full answer. The Code is. O redundant but not ambiguous.
It is found in DNA. Both DNA and RNA. The genetic code is described as what.
The genetic code once thought to be identical in all forms of life has been found to diverge slightly in certain organisms and in the mitochondria of some eukaryotes. Here are some discoveries you can make on the app after youve purchased an AncestryDNA test. Although it is a much harder topic or even a concept to get a good grasp on it is important that a student of biology pays much attention to it.
Which of the following best descrites an example of how genetic codes of organisms have been used to help hierarchically classity living things. The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded in genetic material DNA or RNA sequences is translated into proteins amino acid sequences by living cells. Nucleotides are the building blocks of.
64 codons are quite adequate to specify 20 proteinous amino acids. Organism differ according to the arrangement of the nucleotide bases. It is found in the cell membrane.
The genetic code is the code our body uses to convert the instructions contained in our DNA the essential materials of life. Cells decode mRNAs by reading their nucleotides in groups of three called codons. Genetic code is redundant because.
Neither ambiguous nor redundant. 143 How Is the Information Content in DNA Transcribed to. A The common nucleic acid sequences of polar bears and black bears can be deduced from their classification in the same genus Ursus.
The genetic code can be defined as the set of certain rules using which the living cells translate the information encoded within genetic material DNA or mRNA sequences. The genetic code is best described as. One start codon AUG marks the beginning of a protein and also encodes the amino acid methionine.
A genetic code is one such set of rules which determines how the sequence of the proteins of amino acids should go. The genetic code refers to the DNA alphabet A T C G the RNA alphabet A U C G and the polypeptide alphabet 20 amino acids. It is a nucleic acid.
Adenine A cytosine C guanine G and thymine T in various ways to spell out three-letter codons that specify which amino acid is needed at each position within a protein. This is considered to be nonoverlapping and comma-less. The four nucleotide bases are adenosine thymidine cytidine and guanosine.
Characteristic Of Genetic Code Characteristics Of The Genetic Code A Level Biology Revision Notes Genetic Code. Each amino acid is defined by a three-nucleotide sequence called the triplet codon. Here are some features of codons.
Redundant but not ambiguous. The genetic code is a set of rules defining how the four-letter code of DNA is translated into the 20-letter code of amino acids which are the building blocks of proteins. The central dogma describes the flow of genetic information in the cell from genes to mRNA to proteins.
It allows parents and their young to have similar characteristics. Redundant but not ambiguous. What is the flow of genetic information from DNA to protein.
The properties of genetic code determined by extensive experimental evidences may be summarized as follows. Contains over 3 billion base pairs can help explain genetic diseases and. Redundant in prokaryotes but ambiguous in eukaryotes.
Codons in an mRNA are read during translation. Ambiguous but not redundant. Most codons specify an amino acid.
The ribosomes are responsible to accomplish the process of translation. Though the linear sequence of nucleotides in DNA contains the information for protein sequences proteins are not made directly from DNA. Both ambiguous and redundant.
DNA gene 3-5 DNA template strand transcription mRNA 5-3 triplet code words translation on. The genetic code is called a universal code because all known organisms use the same four nucleotide bases.

Characteristics Of The Genetic Code A Level Biology Revision Notes

0 Comments